Table Of Content
Natural sources of atmospheric CO2include outgassing from volcanoes, the combustion and natural decay of organic matter, and respiration by aerobic (oxygen-using) organisms. These sources are balanced, on average, by a set of physical, chemical, or biological processes, called “sinks,” that tend to remove CO2 from the atmosphere. Significant natural sinks include terrestrial vegetation, which takes up CO2 during photosynthesis.
What can we do to reduce GHG emissions?
While WA had the biggest emissions rise, a few other states also saw an uptick in emissions in 2022 compared with the previous year. By comparison, emissions in Queensland, another big mining state, were 35 per cent lower in 2022 than they were in 2005. As more researchers in different regions work on similar GHG projects, there will be more opportunities for national and international comparisons of progress in dairy GHG emissions. White House officials have renewed discussions about potentially declaring a national climate emergency, an unprecedented step that could unlock federal powers to stifle oil development.
Transportation Sector Emissions
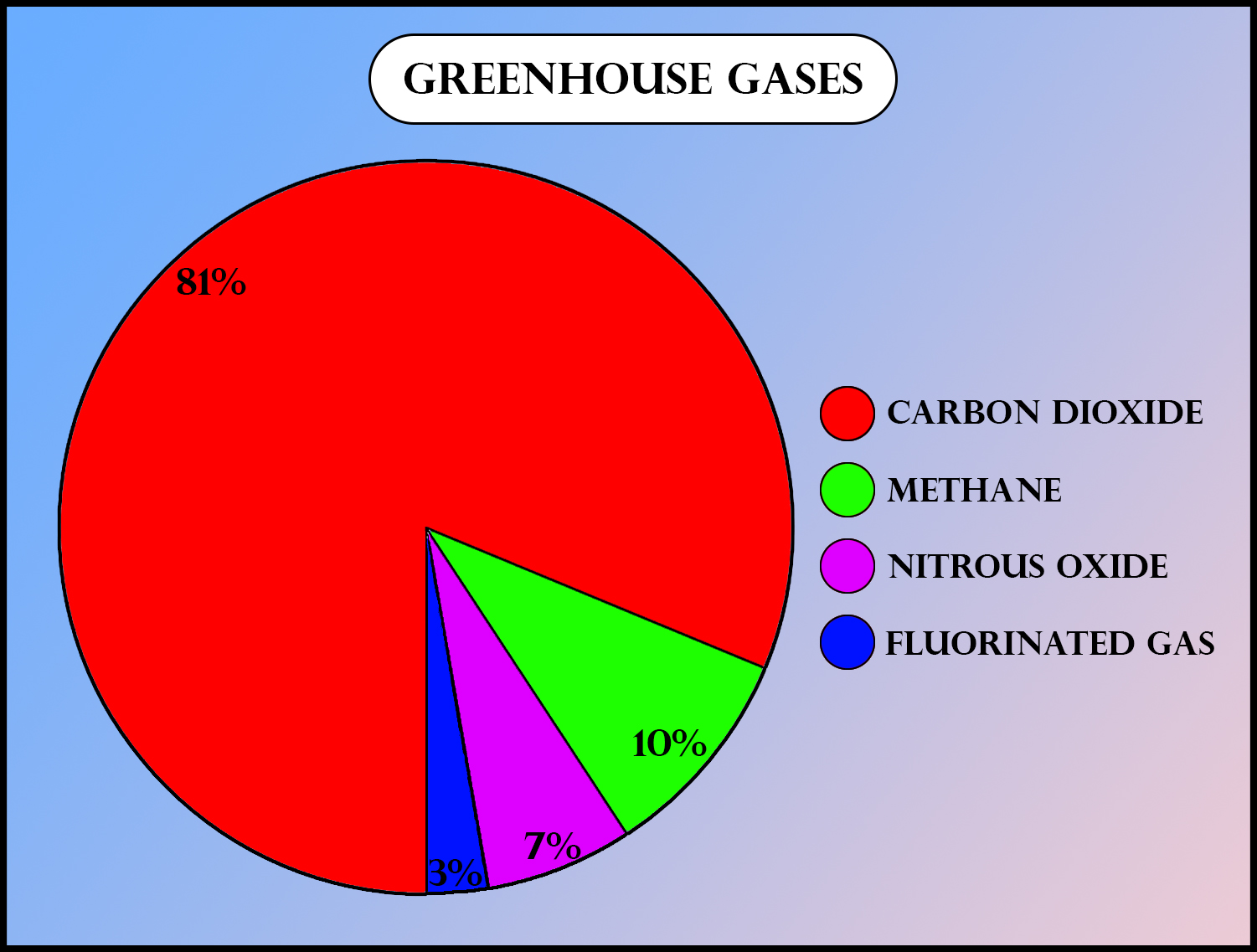
Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per ton emitted, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming Earth. The EPA labeled carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses a danger to public health and welfare 15 years ago. But legal challenges from fossil fuel interests and their allies delayed the finalization of rules to limit climate-warming gasses from the power sector. Greenhouse gases are nothing but gases present in the atmosphere that have the ability to absorb infrared radiations.
‘It’s now or never’: UN climate report’s 4 urgent takeaways
Anthropogenic emissions currently account for the annual release of about 7 gigatons (7 billion tons) of carbon into the atmosphere. Anthropogenic emissions are equal to approximately 3 percent of the total emissions of CO2 by natural sources, and this amplified carbon load from human activities far exceeds the offsetting capacity of natural sinks (by perhaps as much as 2–3 gigatons per year). Other anthropogenic sources include the burning of forests and the clearing of land. Anthropogenic emissions are equal to approximately 3 percent of the total emissions of CO2 by natural sources, and this amplified carbon load from human activities far exceeds the offsetting capacity of natural sinks (by perhaps as much as 2–3 gigatons per year). This is why Earth is often called the 'Goldilocks' planet – its conditions are just right, not too hot or too cold, allowing life to thrive.
While fluorinated gases are far less prevalent than other GHGs and do not deplete the ozone layer like CFCs, they are still very powerful. Over a 20-year period, the global warming potential of some fluorinated gases is up to 16,300 times greater than that of CO2. Other greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, are emitted by human activity, at an unnatural and unsustainable level, but the molecules do occur naturally in Earth's atmosphere. Most of the CO2 that people put into the atmosphere comes from burning fossil fuels. Another way humans release CO2 into the atmosphere is by cutting down forests, because trees contain large amounts of carbon.
The Causes of Climate Change
Anthropogenic aerosols mask increases in US rainfall by greenhouse gases - Nature.com
Anthropogenic aerosols mask increases in US rainfall by greenhouse gases.
Posted: Thu, 22 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
In 2020, global carbon dioxide emissions fell 6.4% (13% in the U.S. alone) — the first time in decades the annual rate hasn’t climbed, Nature reported. This was in part due to the decrease in fossil fuel combustion resulting from the switch to natural gas from coal, but largely because of the forced standstill in economic, social and transportation activities in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Scientists expected the annual emissions decline to actually be larger than it was, but emissions rebounded as restrictions were lifted in some nations and activities recovered toward the end of 2020. The Transportation sector includes the movement of people and goods by cars, trucks, trains, ships, airplanes, and other vehicles. The majority of greenhouse gas emissions from transportation are carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions resulting from the combustion of petroleum-based products, like gasoline and diesel fuel, in internal combustion engines. The largest sources of transportation-related greenhouse gas emissions include passenger cars, medium- and heavy-duty trucks, and light-duty trucks, including sport utility vehicles, pickup trucks, and minivans.
Additional compounds in the atmosphere including solid and liquid aerosol and other greenhouse gases, such as water vapor and ground-level ozone can also impact the climate. Learn more about these compounds and climate change on our Basics of Climate Change page. The Conemaugh Generating Station in New Florence, Pa., is among the nation's coal-fired power plants that face tough new regulations to limit planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions. That change has increased the severity and frequency of storms, heat waves, wildfires and heavy rains.
Radiative forcing
Explore EPA's state and tribal greenhouse gas data and explore resources for states and tribes to develop inventories. Sources of Greenhouse Gases »See the human activities that add GHGs to our atmosphere and options to cut emissions. If all of this ice melted, sea levels would rise by about 70 meters (230 feet). Perhaps the biggest, most obvious effect is that glaciers and ice caps melt faster than usual. The Greenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeEven slight increases in average global temperatures can have huge effects.
Commercial and Residential Sector Emissions Trends
In a report released last year, the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst’s Office, which advises state lawmakers, estimated that emissions had been falling an average of about 1% a year over the last decade and would need to fall 4% annually. That report said the California Air Resources Board lacked “a clear strategy” for meeting the 2030 goal. The chairwoman of the California Air Resources Board — the agency tasked with overseeing greenhouse gas reductions — has taken issue with the study’s conclusion and insists that California is on track to meet its goals. In preparation for each new edition of the inventory, recalculations are made to correct errors, incorporate new methodologies or, most commonly, to reflect changes in statistical data supplied by other agencies. Emission estimates are recalculated for all years to maintain a consistent time-series following IPCC recommendations for developing GHG inventories.
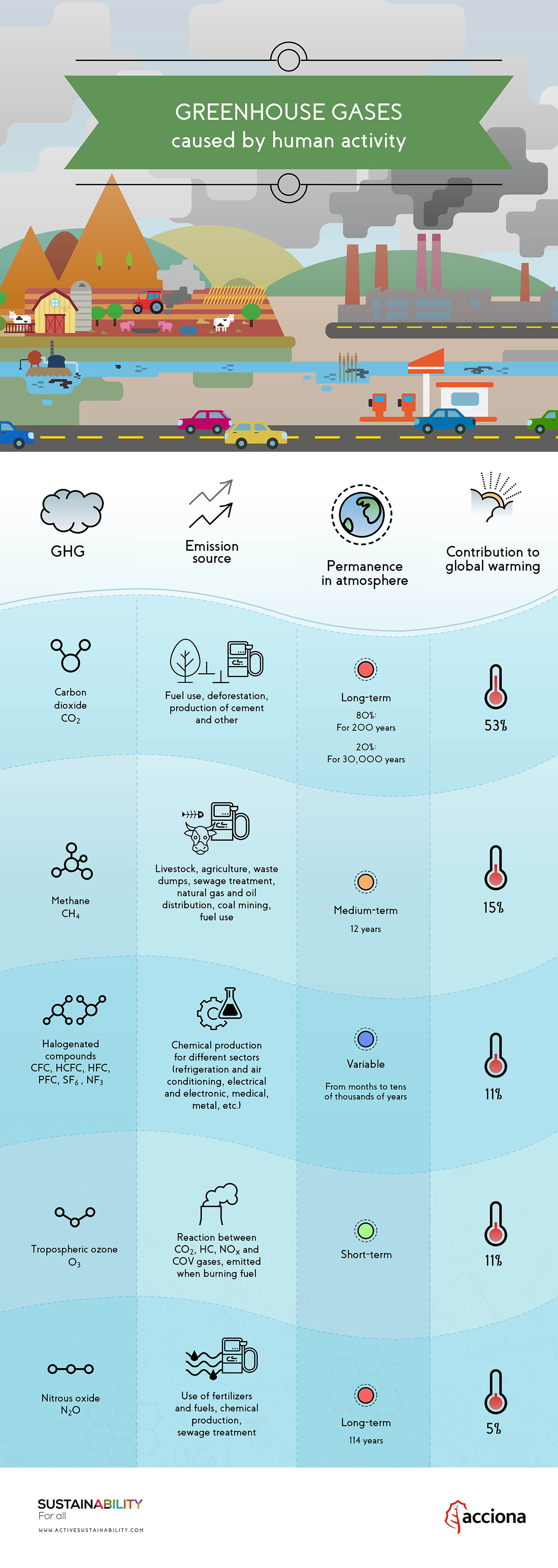
As a result, increased evaporation leads to a greater concentration of water vapour in the lower atmosphere capable of absorbing infrared radiation and emitting it back to the surface. Carbon dioxide emissions in the United States decreased by 2% between 1990 and 2022. Since the combustion of fossil fuel is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, changes in emissions from fossil fuel combustion have historically been the dominant factor affecting total U.S. emission trends.
There are a number of well established, low-cost methods to reduce greenhouse gases from consumer waste, including recycling programs, waste reduction programs, and landfill methane capture programs. Indirect emissions are produced by burning fossil fuel at a power plant to make electricity, which is then used by an industrial facility to power industrial buildings and machinery. Now that we have looked at which countries and sectors emit the most greenhouse gases, there is another way to look at emissions that combines the two. We can look at how companies—both private and government-owned—contribute to climate change.
Despite carbon dioxide’s comparatively low GWP among major greenhouse gases, the large human-caused increase in its atmospheric concentration has caused the majority of global warming. Likewise, methane is responsible for a large portion of recent warming despite having a GWP much lower than several other greenhouse gases because emissions have increased drastically. According to NOAA’s Climate.gov, over the past 60 years, atmospheric CO2 has increased at an annual rate that's 100 times faster than previous natural increases.
EPA also supports the Global Methane Initiative, an international partnership encouraging global methane reduction strategies. Reducing personal energy use by turning off lights and electronics when not in use reduces electricity demand. Improving the insulation of buildings, traveling in more fuel-efficient vehicles, and using more efficient electrical appliances are all ways to reduce energy use, and thus CO2 emissions.

No comments:
Post a Comment