Table Of Content

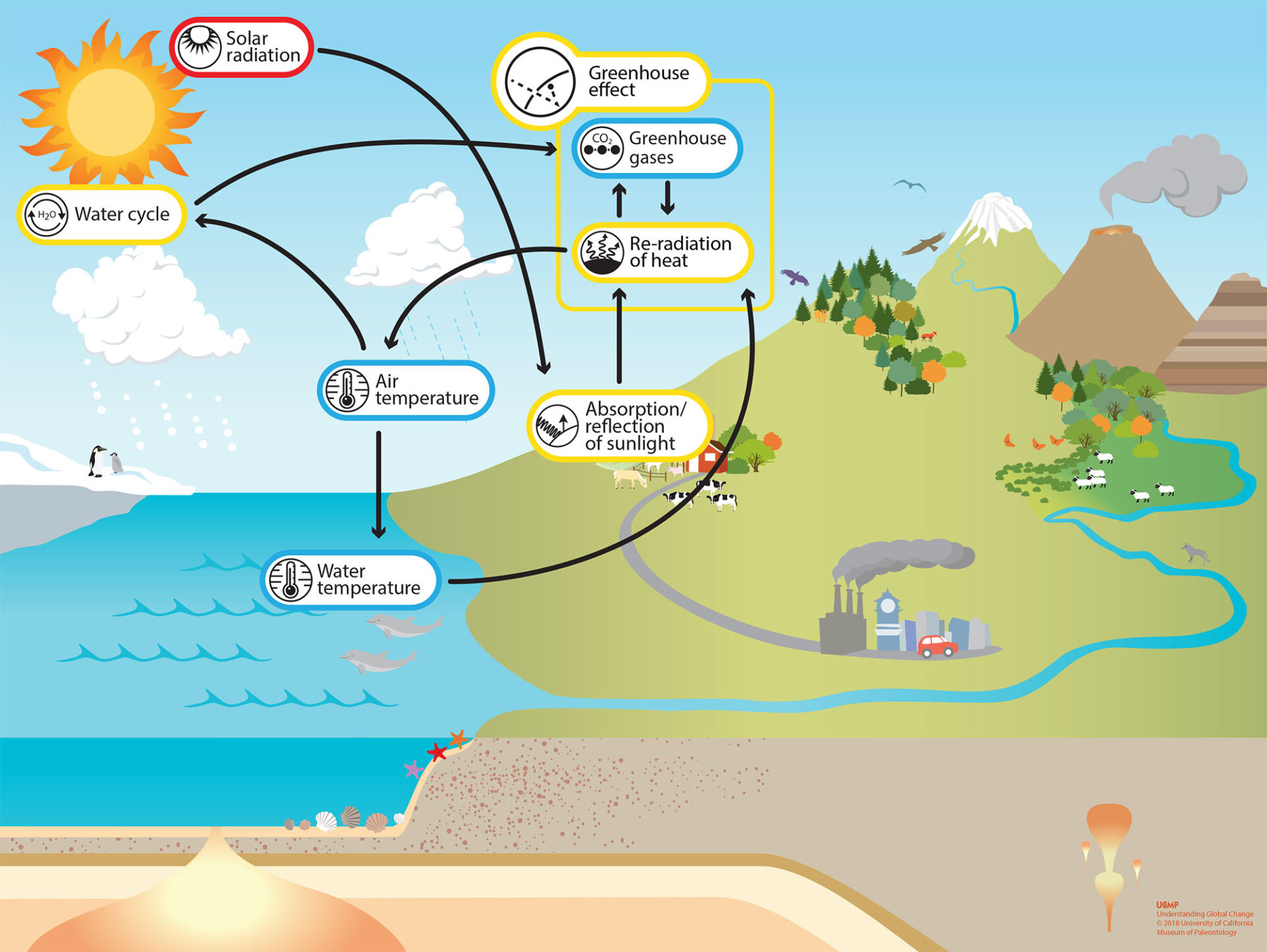
Greenhouse gases allow the sun’s light to shine onto Earth’s surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth’s atmosphere. The gases act like the glass walls of a greenhouse—thus the name, greenhouse gas. Upgrading the equipment used to produce, store, and transport oil and natural gas can reduce many of the leaks that contribute to CH4 emissions. Learn more about the EPA's Natural Gas STAR Program and Coalbed Methane Outreach Program.
Reducing Emissions from Transportation
But the EPA finds those costs would largely be offset by government financial incentives and because technology tends to get cheaper over time. Bapna predicts the new power plant rules will also "drive up investment, innovation, and good jobs in the clean energy economy of the future" and give industry the certainty it "needs to meet growing demand in the cleanest, cheapest, most reliable way possible." While the California plants are marginally more efficient than the average American cement factory, they emit about 33% more pollutants than those in China and India, the report said. Despite the report’s prognosis, authors acknowledged that California is the third-most carbon-efficient state, after New York and Massachusetts. California’s carbon intensity is 8.8% lower than the national average, according to the report. “Our preliminary data show that in 2022 the emissions started to move back down,” said Liane Randolph, who was appointed to lead the board by Gov. Gavin Newsom.
greenhouse effect
EPA’s light-duty and heavy-duty vehicle standards provided incentives for manufacturers to produce vehicles with lower HFC emissions. Globally, 40% of total N2O emissions come from human activities.2 Nitrous oxide is emitted from agriculture, land use, transportation, industry, and other activities, described below. Globally, 50-65% of total CH4 emissions come from human activities.2 Methane is emitted from energy, industry, agriculture, land use, and waste management activities, described below. “Manure treatment and storage is a significant source of GHG emissions on dairy farms that store manure to protect water quality,” Czymmek noted.

343 million metric tons of CO2: What does that mean?
Climate disruption is also causing sea level rise, ocean acidification, plant and animal species extinction and permafrost melting. As the level of greenhouse gas pollution in Earth’s atmosphere continues to rise, these effects will worsen. Researchers around the world continue to work toward finding ways to lower greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate their effects. One potential solution scientists are examining is to suck some of the carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and bury it underground indefinitely. Advocates argue that carbon capture and storage is technologically feasible, but market forces have prevented widespread adoption.
The amount of CO2 in the atmosphere far exceeds the naturally occurring range seen during the last 650,000 years. For further discussion of GWPs and an estimate of GHG emissions using updated GWPs, see Annex 6 of the U.S. The U.S. Inventory uses metric units for consistency and comparability with other countries. For reference, a metric ton is slightly more (approximately 10%) than a U.S. "short" ton.
GWP measures the warming impacts of a gas compared to CO2; it measures the ‘strength’ of the greenhouse gas averaged over a chosen time horizon. The standard way to do this is to evaluate the GWP over a 100-year timescale (GWP100). GWP100 is the accounting metric adopted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in inventory guidelines, although their Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) did not explicitly recommend its use. Chapter 8 of this report described both GWP and Global Temperature-change Potential (GTP) as examples of different metrics that were useful depending on the question being asked.
Emissions of Greenhouse Gases in the Manufacturing Sector - Congressional Budget Office
Emissions of Greenhouse Gases in the Manufacturing Sector.
Posted: Wed, 28 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
List of Ozone Depleting Substances
This storage of carbon in plants, dead organic matter/litter and soils is called biological carbon sequestration. Because biological sequestration takes CO2 out of the atmosphere and stores it in these carbon pools, it is also called a carbon "sink." Examining emissions per capita also exposes differences among top annual greenhouse gas emitters. For example, the United States’ per capita emissions are more than eight times those of India. Although the United States and India rank high in terms of annual emissions, India and neighboring China both have much lower per capita emissions given their large populations (each exceeding one billion). Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect"1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
When a team of Johns Hopkins scientists set out to map exactly where the gas was being released, they were startled to find that California generated as much as 12% of global emissions of the synthetic fumigant. So, instead, the EPA has created regulations governing individual power plants. The agency and environmental groups believe that will allow the rules to survive scrutiny from a court dominated by conservative justices.
According to ice core measurements, such levels are believed to be the highest in at least 800,000 years and, according to other lines of evidence, may be the highest in at least 5,000,000 years. The effect of each greenhouse gas on Earth’s climate depends on its chemical nature and its relative concentration in the atmosphere. Some gases have a high capacity for absorbing infrared radiation or occur in significant quantities, whereas others have considerably lower capacities for absorption or occur only in trace amounts. To understand the relative influence of each greenhouse gas, so-called forcing values (given in watts per square metre) calculated for the time period between 1750 and the present day are given below.
The report found that GHG emissions need to be halved by 2030, if we are to limit global warming to 1.5°C compared to pre-industrial levels by the end of the century. Without the heating caused by the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average surface temperature would be only about −18 °C (0 °F). On Venus the very high concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes an extreme greenhouse effect resulting in surface temperatures as high as 450 °C (840 °F).
The GWP100 value for methane from AR5 is 28 (or 34 if climate feedback processes are included).8 This means that emitting one kilogram of methane creates 28 times the amount of warming as one kilogram of CO2 averaged over the next 100 years. But what this doesn’t account for is the fact that methane is a short-lived greenhouse gas. It has a very strong warming impact when it is first emitted, but this warming impact diminishes over the following decades. Whereas, if you emitted the same amount of CO2, it could persist for centuries.

No comments:
Post a Comment